If you are a small business looking to be found on search engines, then optimizing your site and brand online is crucial.
Before we get started, I just wanted to make a couple of points clear. First, there is no quick way to get ranked on search engines. Doing SEO takes time, dedication, and consistency. Second, always keep in mind that the goal of a search engine is to show the most relevant results and to deliver the best user experience to a searchers query.
It is important that we start with those two points as I will reference both of these throughout the article.
So, if you are reading this article, it means you want to be found by consumers when they search for a product or service that you offer. For small businesses, your goal should be to found on the “local 3 pack” and search engine results.

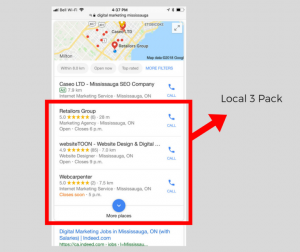
Local 3 pack refers to the maps that show up typically after paid ads and just before search results. Google usually shows the top 3 local businesses that they deem the most relevant based on what someone searched for. Efforts to optimize your online presence and show up on local map results are often referred to as local SEO.
Search engine results on the other hand give searchers a set of links to web pages that Google deems the most relevant to the user’s query. These can be links to company websites or articles posted on blogs. It can even lead to directory listings or even job postings. Once again, Google will deliver the results based on what they feel the user’s intention was when they made their query.
Now that we know what we are trying to accomplish, let’s get to it!
Here are some steps on how to rank a small business on Google:
1) Assess your Current Digital Marketing Presence
Before you start making all of these efforts to rank on Google, you should really take a step back to assess where you currently stand.
Do you have a website? If no, that would probably be a good place to start. We wrote a previous article on how to establish your online presence.
If you do have a website, you need to make sure that it is mobile friendly and that your speed load times are at a good level.
Google provides tools to check these out. Mobile friendly test here, and load time test here.
Why are these important? As stated at the top, Google wants to deliver a good user experience. Fast load times and being able to access your website on a mobile device both equate to good user experience.
Fixing these two areas can make big improvements in how you rank.
Next up, if you are a local business looking to rank on the local 3 pack, let’s make sure you have your Google My Business (GMB) page created and filled out accurately. Create your GMB Page here.
2) On-Page Optimization
Since Google wants to serve up the most relevant results to a search, let’s make sure first off, we are actually delivering the best and most relevant content.
If some of your content is outdated, now would be a good time to update it. Always layout your content to satisfy questions that your potential customer might be asking about your products, services, and even your company.
If you sell multiple products or have various services, it is always best to have separate pages for each one. If for example, you are a mortgage broker, you’ll want to have a separate page for mortgage renewals and another page for equity lines of credit. The idea is to attempt to rank each service separately and cater to a searchers query appropriately.
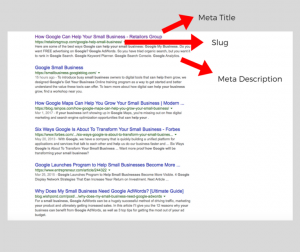
Now that you have your website setup up and ready for search engines to find you, it’s time to optimize the page for Google to better understand what is on it.
There are certain on-page components that Google looks at to better understand what is on this page:
- Slug: This is the URL extension of the page (ie http://yoursite.com/this-is-the-slug)
- Meta Title: this is what Google shows as the title on their search engine results
- Meta Description: this is the description under the title that Google shows on their results
- H1, H2 and other H Titles: These are titles and subtitles found in your content that your visitors will see
- Alt Image Tags: This is a tag that lets Google know what these images on your page is about
- Content: pretty straightforward, your content
- Contact Information using Schema Markup: Schema.org (often called Schema) is a specific vocabulary of tags (or microdata) that you can add to your HTML to improve the way your page is represented in SERPs. (source: https://moz.com/learn/seo/schema-structured-data)
When optimizing your page, you want to make sure there is consistency between your meta title, description, tags, and in your content. Don’t make it spammy!! Find the right balance between designing for your audience and making sure search engines can read it. When stuck, always go with the design for the audience before the search engine.
3) Directory Listing and Social Media Registration
Previously, we stated that you should want to set a goal of ranking in the top three for your business category. We instructed earlier as well to claim or create your Google My Business (GMB) Page, which is what gets listed in the maps for local searches.
Once your GMB page is created and optimized, you want to now be found by both consumers and search engines. In order for Google to confirm who you are, they search the Internet to match up your name, address, and phone number (often referred to as NAP) with as many creditable sources as possible.

A lot of the creditable sources include popular directories like Yelp, Foursquare, Yellow Pages and Better Business Bureau. It is also good to register local business directories. Google also uses social media sites like Facebook, LinkedIn, Twitter and so on as credible sources to confirm who you are.
As your customers start giving you reviews on these directories and you are staying active on social media with relevant and sharable content, Google will begin to recognize and understand more about you. The better they understand you, the better your chances are of getting listed on the local 3 pack.
4) Link Building
Imagine telling a room full of people that you are a great basketball player. If nobody knows who you are, likely nobody will take you seriously either. But as soon as one or two other people in the room confirm your claim, the more creditable you become. The more creditable you become, the more Google trusts you, and the more likely you will be chosen by Google to be a relevant source.
That is basically what you want to achieve with link building; you want more people to create links pointing back to your website. When Google crawls the Internet and finds all of these links pointing to you, it is the equivalent to my analogy above of people in a room confirming you are the best basketball player.
Now, if your mom is the one confirming you are the best basketball player, you might not gain too much creditability. If Michael Jordan on the other hand confirms your claim, you can be sure that people, including Google, will listen.
So how do we get authoritative sources to link back to your website? That’s an article on its own, but what you do want to focus on is what you are in control of; creating great and sharable content.
Let’s make sure your website has a blog where you can teach and educate people or your product or service. In those blogs, you can create what is called internal links pointing back to relevant areas of your website. Search engines love when they serve up a relevant article that a user reads and continues to click through to links as opposed to hitting the back button on their browser.
In these blogs, give credit where credit is due. If you referenced an idea or took a quote from someone, create a link for them. Good karma will eventually come back your way when others reference your great content.
Share these blogs on social media and make sure your content is search engine friendly. The more people that read your articles, the better chance you get on either converting the user to a customer or getting a backlink to your website.
5) Submit sitemaps to Google and Bing
Both Google and Bing have tools to help them understand more about you. We wrote a guide on Google Search Consoles here. Bing has a similar tool called Bing Webmaster tools.
Basically, these tools allow you to submit a sitemap, which is essentially a list of the pages on your website. You can even speed up the crawling process of your website with these tools.
There are a ton of other resources available on Google Search Console and Bing Webmaster Tools which can help optimize your site and give valuable information like search queries, impressions, click-through-rates, and average position on rankings.
6) Analyze and Make Necessary Adjustments
All of these efforts you make to be found by Google can be exhausting. Worst yet, if you are not making progress, it can be frustrating.
It is crucial that you track your progress and make necessary adjustments. Google provides great tools to make sense of your SEO efforts.
Google Search Console, as mentioned above is a great tool to track everything about search results. Google My Business has a dashboard that gives great insights into how users interact with your GMB page. Google also has an extensive analytics tool, appropriately called Google Analytics, that gives a lot of in-depth information on user behavior and demographics of visitors coming to your website.
There are also a ton of SEO analysis tools available to check out. Relevance.com did a good summary here of 5 of those tools.
As you can see, doing SEO yourself can be daunting but it is totally doable. You don’t need to be an expert or have a bachelor’s degree to rank high on search engines. All you need is time, dedication, consistency, and follow these steps.
About Retailors Group
The team at Retailors Group has over 15 years of retail sales and field marketing experience. Retailors Group takes the time to understand your brand and align your core values into a tailor-made solution that builds a long-lasting relationship with your consumers.
We offer services in Experiential Field Marketing, On-site Sales Assist, Retail Management and Digital Marketing.
